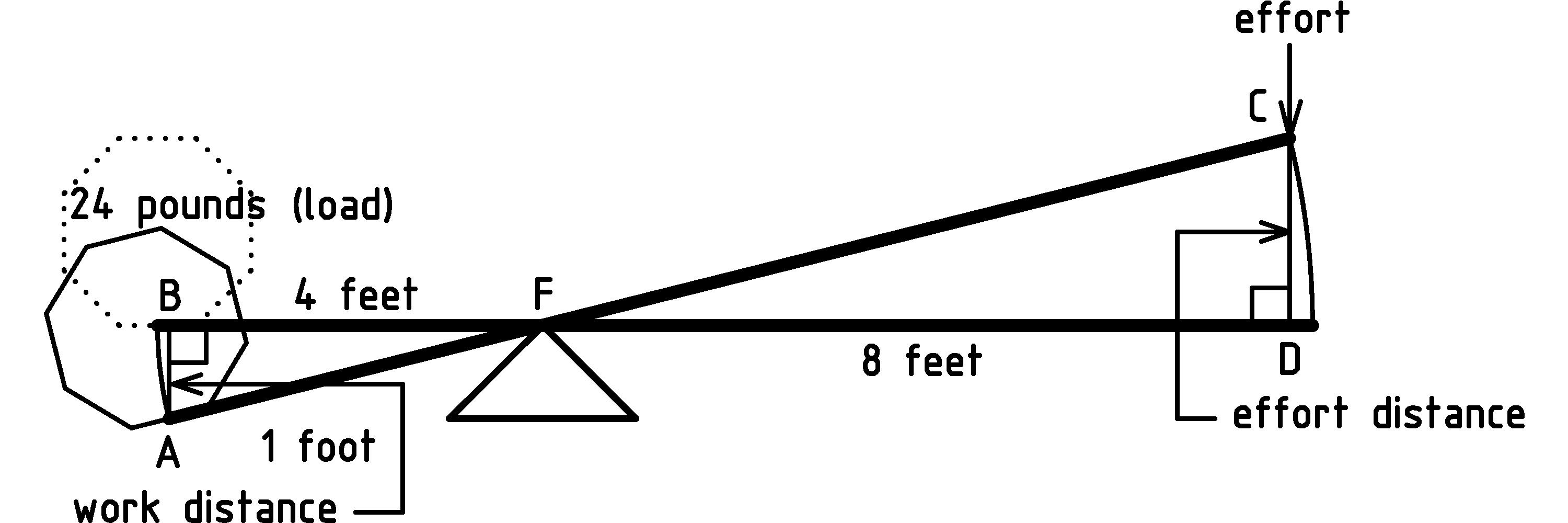
Lever Balance Equation . A beam of length l is balanced on a pivot point that is placed directly beneath the center of mass of the beam. Once students understand the physical principles behind the lever, they can consider how to use. the balanced equation looks like fin ∗din = fout ∗dout f i n ∗ d i n = f o u t ∗ d o u t, which can be rearranged to define the mechanical advantage. The beam will not undergo rotation if the product of the normal force with the moment arm to the pivot is the same for each body, \[d_{1} n_{1}=d_{2} n_{2} \nonumber \] the lever equation defines the forces and the physical features of a lever in its equilibrium status. It derives from the comparison of the torque. this lever mechanical advantage equation and calculator case #1 will determine the force required for equilibrium with the known forces and length.
from www.math2learn.org
the lever equation defines the forces and the physical features of a lever in its equilibrium status. The beam will not undergo rotation if the product of the normal force with the moment arm to the pivot is the same for each body, \[d_{1} n_{1}=d_{2} n_{2} \nonumber \] Once students understand the physical principles behind the lever, they can consider how to use. It derives from the comparison of the torque. this lever mechanical advantage equation and calculator case #1 will determine the force required for equilibrium with the known forces and length. A beam of length l is balanced on a pivot point that is placed directly beneath the center of mass of the beam. the balanced equation looks like fin ∗din = fout ∗dout f i n ∗ d i n = f o u t ∗ d o u t, which can be rearranged to define the mechanical advantage.
Forces, Work, and Simple Machines
Lever Balance Equation the lever equation defines the forces and the physical features of a lever in its equilibrium status. Once students understand the physical principles behind the lever, they can consider how to use. the balanced equation looks like fin ∗din = fout ∗dout f i n ∗ d i n = f o u t ∗ d o u t, which can be rearranged to define the mechanical advantage. the lever equation defines the forces and the physical features of a lever in its equilibrium status. this lever mechanical advantage equation and calculator case #1 will determine the force required for equilibrium with the known forces and length. A beam of length l is balanced on a pivot point that is placed directly beneath the center of mass of the beam. It derives from the comparison of the torque. The beam will not undergo rotation if the product of the normal force with the moment arm to the pivot is the same for each body, \[d_{1} n_{1}=d_{2} n_{2} \nonumber \]
From www.vecteezy.com
Different types of levers with examples vector illustration 23452904 Lever Balance Equation the lever equation defines the forces and the physical features of a lever in its equilibrium status. A beam of length l is balanced on a pivot point that is placed directly beneath the center of mass of the beam. Once students understand the physical principles behind the lever, they can consider how to use. It derives from the. Lever Balance Equation.
From www.alamy.com
Illustration of the simple lever balance Stock Vector Image & Art Alamy Lever Balance Equation It derives from the comparison of the torque. The beam will not undergo rotation if the product of the normal force with the moment arm to the pivot is the same for each body, \[d_{1} n_{1}=d_{2} n_{2} \nonumber \] Once students understand the physical principles behind the lever, they can consider how to use. A beam of length l is. Lever Balance Equation.
From www.dreamstime.com
Lever Vector Illustration. Labeled Physical Formula Explanation Scheme Lever Balance Equation It derives from the comparison of the torque. this lever mechanical advantage equation and calculator case #1 will determine the force required for equilibrium with the known forces and length. Once students understand the physical principles behind the lever, they can consider how to use. the balanced equation looks like fin ∗din = fout ∗dout f i n. Lever Balance Equation.
From www.thoughtco.com
The Physics Behind How a Lever Works Lever Balance Equation this lever mechanical advantage equation and calculator case #1 will determine the force required for equilibrium with the known forces and length. the balanced equation looks like fin ∗din = fout ∗dout f i n ∗ d i n = f o u t ∗ d o u t, which can be rearranged to define the mechanical advantage.. Lever Balance Equation.
From www.chegg.com
What makes a lever balanced? Many machines use the Lever Balance Equation It derives from the comparison of the torque. this lever mechanical advantage equation and calculator case #1 will determine the force required for equilibrium with the known forces and length. Once students understand the physical principles behind the lever, they can consider how to use. The beam will not undergo rotation if the product of the normal force with. Lever Balance Equation.
From dxoqqhkuz.blob.core.windows.net
Lever Equations at Brent Lee blog Lever Balance Equation The beam will not undergo rotation if the product of the normal force with the moment arm to the pivot is the same for each body, \[d_{1} n_{1}=d_{2} n_{2} \nonumber \] Once students understand the physical principles behind the lever, they can consider how to use. the balanced equation looks like fin ∗din = fout ∗dout f i n. Lever Balance Equation.
From dxoqqhkuz.blob.core.windows.net
Lever Equations at Brent Lee blog Lever Balance Equation the balanced equation looks like fin ∗din = fout ∗dout f i n ∗ d i n = f o u t ∗ d o u t, which can be rearranged to define the mechanical advantage. The beam will not undergo rotation if the product of the normal force with the moment arm to the pivot is the same. Lever Balance Equation.
From www.shutterstock.com
Law Lever Formula Lever Balance Stock Vector (Royalty Free) 2014966931 Lever Balance Equation the lever equation defines the forces and the physical features of a lever in its equilibrium status. It derives from the comparison of the torque. A beam of length l is balanced on a pivot point that is placed directly beneath the center of mass of the beam. The beam will not undergo rotation if the product of the. Lever Balance Equation.
From kinesiologykris.com
The 3 Classes of Levers Lever Balance Equation the balanced equation looks like fin ∗din = fout ∗dout f i n ∗ d i n = f o u t ∗ d o u t, which can be rearranged to define the mechanical advantage. Once students understand the physical principles behind the lever, they can consider how to use. It derives from the comparison of the torque.. Lever Balance Equation.
From dxowoygat.blob.core.windows.net
What Are The Classes Of Lever And Their Examples at Jose Rachel blog Lever Balance Equation the lever equation defines the forces and the physical features of a lever in its equilibrium status. this lever mechanical advantage equation and calculator case #1 will determine the force required for equilibrium with the known forces and length. It derives from the comparison of the torque. the balanced equation looks like fin ∗din = fout ∗dout. Lever Balance Equation.
From dxoqqhkuz.blob.core.windows.net
Lever Equations at Brent Lee blog Lever Balance Equation the lever equation defines the forces and the physical features of a lever in its equilibrium status. It derives from the comparison of the torque. A beam of length l is balanced on a pivot point that is placed directly beneath the center of mass of the beam. the balanced equation looks like fin ∗din = fout ∗dout. Lever Balance Equation.
From www.shutterstock.com
Lever Formula Equilibrium Two Different Heavy Stock Vector (Royalty Lever Balance Equation this lever mechanical advantage equation and calculator case #1 will determine the force required for equilibrium with the known forces and length. It derives from the comparison of the torque. the lever equation defines the forces and the physical features of a lever in its equilibrium status. Once students understand the physical principles behind the lever, they can. Lever Balance Equation.
From www.dreamstime.com
Lever and Formula of Balance Stock Vector Illustration of equilibrium Lever Balance Equation Once students understand the physical principles behind the lever, they can consider how to use. The beam will not undergo rotation if the product of the normal force with the moment arm to the pivot is the same for each body, \[d_{1} n_{1}=d_{2} n_{2} \nonumber \] A beam of length l is balanced on a pivot point that is placed. Lever Balance Equation.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Phase Equilibrium PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6592593 Lever Balance Equation The beam will not undergo rotation if the product of the normal force with the moment arm to the pivot is the same for each body, \[d_{1} n_{1}=d_{2} n_{2} \nonumber \] Once students understand the physical principles behind the lever, they can consider how to use. this lever mechanical advantage equation and calculator case #1 will determine the force. Lever Balance Equation.
From www.scienceinschool.org
Balancing act the physics of levers Science in School Lever Balance Equation It derives from the comparison of the torque. this lever mechanical advantage equation and calculator case #1 will determine the force required for equilibrium with the known forces and length. A beam of length l is balanced on a pivot point that is placed directly beneath the center of mass of the beam. the balanced equation looks like. Lever Balance Equation.
From physicscalculations.com
What is a Lever Balance in Physics? Lever Balance Equation Once students understand the physical principles behind the lever, they can consider how to use. this lever mechanical advantage equation and calculator case #1 will determine the force required for equilibrium with the known forces and length. It derives from the comparison of the torque. A beam of length l is balanced on a pivot point that is placed. Lever Balance Equation.
From www.youtube.com
9th Class Physics, Ch 01, Lever Balance Physics 9th Matric Part 1 Lever Balance Equation the lever equation defines the forces and the physical features of a lever in its equilibrium status. It derives from the comparison of the torque. The beam will not undergo rotation if the product of the normal force with the moment arm to the pivot is the same for each body, \[d_{1} n_{1}=d_{2} n_{2} \nonumber \] A beam of. Lever Balance Equation.
From owlcation.com
Simple Machines — How Does a Lever Work? Owlcation Lever Balance Equation this lever mechanical advantage equation and calculator case #1 will determine the force required for equilibrium with the known forces and length. It derives from the comparison of the torque. the balanced equation looks like fin ∗din = fout ∗dout f i n ∗ d i n = f o u t ∗ d o u t, which. Lever Balance Equation.